IB Economics
Distribution of Income – All in One Go
Sep 15th
In just one post, I include resources for the section of the IB Eco syllabus (2005 version) called 3.6 Distribution of Income.
The topic includes the following points:
• Direct taxation
• Indirect taxation
• Progressive taxation
• Proportional taxation
• Regressive taxation
• Transfer payments
Higher level extension topics
• Laffer curve
• Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient
Use the following resources to learn about these sub-topics:
Direct versus Indirect
Compare these two definitions:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_tax
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indirect_tax
Can you explain the difference between direct and indirect tax with example taxes?
Progressive, Regressive, and Proportional Tax
ONE Massachusetts (ONEMassPPI) demonstrates the different types of taxes:
Specific Examples of Taxation
This mjmfoodie video includes specific examples of US taxes, then a section on how taxes relates to the government’s budget (which is worth understanding in general terms) and finally a section reviewing the general types of taxes.
Testing Your Understanding of Taxes
A ‘tic tac toe’ game which puts some of the above to the test but you may also need to use your common sense and a bit of guesswork. Play as two people.
Sort different types of taxes using reffonomics here.
Transfer Payments
Check wikipedia on the matter.
And there is a brief definition courtesy of BusinessDictionary.com here
This is interesting on the increasing % spent on Transfer payments in the US since 1930:
http://mjperry.blogspot.com/2011/08/chart-of-day-transfer-payments.html
Laffer Curve
by pajholden
by
Lorenz curve and Gini coefficient
Use this video by pajholden.
And this one by EconInstructor:
Or this very short one:

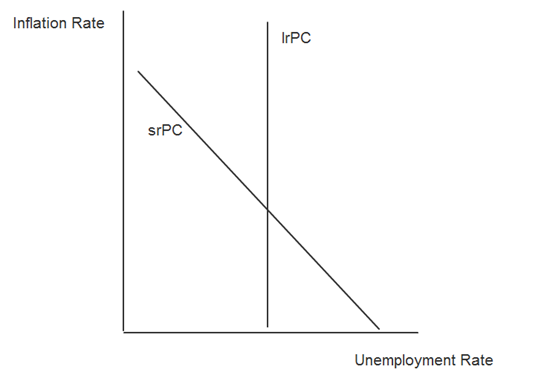
The Phillips Curve
Sep 14th
Be warned. This one’s quite tricky. We’ll rely heavily on the truly excellent http://www.reffonomics.com website for this topic, but these activities will be best used following some prior learning of the Phillips Curve. I like the approach that reffonomics take, it is thorough and helps to give a good recap of general ASAD macro models. This takes things to quite an advanced level though.
First, learn about (or recap) the topic by visiting this eye-catching interactive.
Second, run through this presentation and see if you give correct answers for the short series of questions.
Third, try your hand at this quiz.
Fourth, explore how different scenarios impact on the ASAD graph and the Phillips Curve Graph here.
Fifth, try 20 multiple choice questions here. Some of them are tricky, but you’ll get instant feedback at the end.
Lastly, try your hand at some of these activities here – have a go by moving the lines and A, B and C points, and then see the suggested answers. You might not understand how to do the first one or two, but when you see their animated answers you should hopefully begin to get the hang of it.
Advanced activity:
Step 1 – download this ‘free response’ worksheet and answer using good old pencil / ruler combo.
Step 2 – check your answers against these suggested answers.
Data Response Question – Unemployment
Sep 6th
For those studying IB Economics, this is a data response question which I created for the unemployment topic back in 2008, following the usual conventions and mark scheme requirements as closely as I could.

Photo: Some rights reserved by Saad.Akhtar
The text is adapted from an original article by The Times Online, but it does not appear to be hosted there anymore.
Click here for the question paper.
Click here for the mark scheme.
Calculating Inflation
Aug 31st
2 handy and thorough videos. The first by pajholden takes a UK perspective:
inflation rates – how they are calculated
Secondly, ACDCLeadership takes a US slant:
This one by Mindbitesdotcom is good on the key differences between the GDP deflator and Consumer Price Index, and the way that different approaches to calculating an index can lead to different values (good for evaluation):
Unemployment Part 1
Aug 18th
Syllabus requirements (first part):
Unemployment
• Full employment and underemployment
• Unemployment rate
• Costs of unemployment
• Types of unemployment
• structural
• frictional
• seasonal
• cyclical/demand-deficient
• real wage
(Macro) Episode 18: Unemployment by mjmfoodie
(Macro) Episode 19: Types of Unemployment by mjmfoodie
Unemployment – Description of different types by jcsballoon
The Multiplier, Accelerator and Crowding Out
Aug 17th
These are Higher Level Extension Topics, and are listed in the following way on the 2005 IB syllabus:
• Multiplier
[including calculation of multiplier]
• Accelerator
• “Crowding out”
Here are some video resources and questions to help you understand these concepts.
Watch the following video and then answer the questions underneath.
MPC and the Multiplier by FitzEcon
1) Define the MPC?
2) What is the formula for the multiplier?
3) Define the MPS.
4) Record, in writing / notes, the example given by the speaker.
5) Extension – Check your text book’s entry and enhance your explanation of the multiplier, with particular attention to the concept of ’rounds’
Fiscal policy and the multiplier effect by pajholden
6) Why, in the example given, does the government want to boost Aggregate Demand?
7) What would be the trade-off of this economic goal?
8] Demonstrate the above on a sketch diagram.
9) What two fiscal policy options does the government have?
10) What does the theory of the multiplier effect state? (add to previous explanation)
11) Briefly summarise the example given of how an initial increase in spending on healthcare by the government leads to further increases in AD.
12) What are the difficulties mentionned which are associated with the multiplier effect?
13) Extension – think about it – why might cutting tax be different in terms of the impact on the multiplier compared to increasing government spending by the same amount of money?
MEC and Accelerator investment theories by pajholden
NOTE You only need to focus on the Accelerator Theory (4 mins 16 secs onwards) for HL IB Economics (although it is harmless to view the MEC theory section)
14) What are the two types of investment mentionned – explain the difference.
15) What is the Accelerator Theory in basic terms.
16) Enhance your notes by checking your text book and following links:
http://tutor2u.net/economics/revision-notes/as-macro-multiplier-accelerator.html
Bottom of this page: http://econ.la.psu.edu/~dshapiro/l18nov04.htm
http://cafehayek.com/2010/02/crowding-out.html
Crowding Out
Research and summarise information to include the following features under the topic of ‘crowding out’. Two useful videos and a slideshow are given at the end.
- Definitions
- Explanation of what it is
- Examples
- Diagrams
- Outline the difference between complete, partial and no crowding out.
(Macro) Episode 27: Crowding Out & Lags by mjmfoodie
Note that from c. 2mins 50 secs moves on to time lags – it is good revision of this separate topic!
A helpful animated slideshow:
Crowding Out Effect by reffonomics.com – click here
And finally, this is pure genius! …
Crowding-Out Effect Song (Heavy Metal Edition) by medicotube
Market Failure
Mar 8th
Introduction to Market Failure
Let’s kick off with mjmfoodie:
economicshelp gives us this video:
Another simple overview of how markets fail for merit and demerit goods (S and D curves used)
BrynJonesOnline:
More complicated overview of market failure using concept of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
richardmckenzie covers welfare loss and briefly introduces solutions at end.
(1 of 2)
(2 of 2)
Externalities
From mjmfoodie:
Follow this link:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S0lH4GEFy1o
Simple Overview of how markets fail for merit and demerit goods (S and D curves used) by BrynJonesOnline
Lighthearted and simple overview of some solutions to negative externalities by ASEconomics
Some student work on the topic:
Public Goods
by mjmfoodie
Price Discrimination
Feb 28th
The first video in this post goes to a student. Komilla (CuteChadz)has produced a very professional looking summary and it is well worth a look:
pajholden does price discrimination
richardmckenzie gives us two videos:
Click here to see a Reffonomics interactive presentation on price discrimination.
For a bit of fun, view the scene from the Monty Python film ‘Life of Brian’ where confusing haggling (first price discrimnation) takes place – click here.
Oligopoly
Feb 21st
IB Syllabus requirements:
• Assumptions of the model
• Collusive and non-collusive oligopoly
• Cartels
• Kinked demand curve as one model to describe interdependent behaviour
• Importance of non-price competition
• Theory of contestable markets
BrynJonesOnline introduces the theory before moving onto Kinked Demand Theory:
Cartels
This helpful video is by richardmckenzie
Non Collusion – Kinked Demand Theory:
An animated slideshow on oligopoly focuses on kinked demand theory (from the excellent Reffonomics ).
The above introduces the ‘kink’ (by ACDCLeadership). The below is by pajholden and goes into more detail:
kinked demand curve theory (click on the link to view)
The kinked demand theory can be extended to show how such a non-collusive oligopolistic firm makes a loss, makes a profit or breaks even (again from the excellent Reffonomics ).
Theory of Contestable Markets
pajholden discusses the theory in his back garden: contestable market theory
economicslessons has produced this video geared towards A Level economics (so the example question at the end is not an IB one):
Extra:
On the interdependency of firms, we should consider John Nash who arrived at the theory of a Nash Equilibrium in which members of a group would serve their own interests by also serving the rest of the group’s interests (as opposed to Adam Smith’s contention that individuals (or firms) will strive to serve their own interests only). This idea was captured in the excellent film A Beautiful Mind and the relevant excerpt can be seen by clicking here.
On the difficulty of drawing a line between monopolistic competition and oligopoly, view this slideshow by Reffonomics.
Finally, for a bit of fun, see how a famous condom manufacturer has approached non-price competition through the power of advertising by clicking here.