Economic Systems
Sep 1st
The three fundamental economic questions:
- What to produce?
- How to produce?
- For whom to produce?
There are three economic systems, we will concentrate for now on the first three:
- Traditional Economy
- Market Economy
- Command or Planned Economy
- Mixed Economy (we will study this later)
Study one of the first three, collaborate with others in a group, and produce something (presentation / video / report) to explain it in as simple terms as possible. Be warned, many of the websites listed below are very complicated. So, as well as these, use your text books, own general research, your teacher if possible, and each other. Make sure you divide your work up fairly between the members of your group.
Here are some guiding questions:
- What is this type of economy?
- How does it answer the three fundamental economic questions? How does it work?
- Who uses a this type of economy? In what parts of the world are they found? Give examples.
- Advantages of a this type of economy?
- Disadvantages of this type of economy?
Traditional Economy
Click here to see some useful websites for researching about traditional economies.
Market Economy
Click here to see some useful websites for researching about market economies.
Power of the Market – Invisible Hand by LibertyPen
Command (or Planned) Economy
Click here to see some useful websites for researching about command (also known as ‘planned’) economies.
General
Click here to see some useful websites which refer to more than one of the economic systems, usually to compare them.
Economics :: Week 11, Part C by icarpcast
If you find any more good websites please email them to me … james@opengecko.com
Calculating Inflation
Aug 31st
2 handy and thorough videos. The first by pajholden takes a UK perspective:
inflation rates – how they are calculated
Secondly, ACDCLeadership takes a US slant:
This one by Mindbitesdotcom is good on the key differences between the GDP deflator and Consumer Price Index, and the way that different approaches to calculating an index can lead to different values (good for evaluation):
Basic Economic Problem–Part 2
Aug 25th
We are still introducing some important concepts (ideas) in Economics while following the IGCSE Economics Syllabus which includes the following requirements:
• define opportunity cost and analyse particular circumstances to illustrate the concept;
• evaluate the implications of particular courses of action in terms of opportunity cost.
Here are two videos designed to introduce the idea of opportunity cost:
Episode 8: Opportunity Cost by mjmfoodie
This light-hearted YouTube clip reinforces the fact that it need not be about money, but that cost in this sense can be measured in time:
What Is Opportunity Cost? by wreuter1
This pdf file is a set of resources for teaching the idea of opportunity cost to young children. You might find it useful, especially the first page and the top of the second page which has questions and their answers.
http://www.kidseconposters.com/images/hp_op_cost.pdf
This page from tutor2u gives a useful overview suitable for IGCSE Economics: click here.
Suggested activity
Perhaps working with one other partner, can you create a short video of your own to illustrate the concept of opportunity cost. Try to present several different scenarios, at different scales. Here are some examples:
- An opportunity cost you might face today
- An opportunity cost you might face at the weekend
- An opportunity cost following a recent decsision by your school
- An opportunity cost linked to a decision made by the government for your country
Technology tip:
You could create a video a bit like the mjmfoodie one at the top. One way of doing this is to have a set of slides with pictures and perhaps a few key words in a powerpoint or google presentation. You need a way of recording your voice and capturing things that are happening on the screen at the same time (such as playing through your finished presentation while you speak over it). This is called a screencast. It is a good idea to write a script for your screencast so that the finished product is as professional as possible.
Quicktime allows you to create screencasts. An online solution (which needs you to already have an account for google, twitter, facebook or a few others to sign in is http://www.screenr.com. On the free plan, you are limited to 5 minutes but that should be an ideal maximum time for this kind of activity anyway. At the end you publish to screenr but you can then download the .mp4 file and delete the online version if you want. Screenr requires you to have java enabled.
Basic Economic Problem – Part 1
Aug 21st
We are introducing some important concepts (ideas) in Economics while following the IGCSE Economics Syllabus which has the following requirements:
|
To help us understand these concepts, we can use some very useful youtube videos and some interactive quizzes and other links.
The Economic Problem (Finite Resources and Unlimited Wants)
Needs and Wants by kathycassidy
Needs and Wants by alamberth
A quiz via http://www.businessstudiesonline.co.uk on Needs or Wants – click here.
Scarcity & Choice by mjmfoodie
Notice the definition given of Economics.
The Economic Problem is also nicely summarised here:
Scarcity by stephenmonrad
The above video has already introduced some of the resources we would need to make the things we want. In Economics, resources are referred to as the Factors of Production …
2) The Factors of Production
Resources by mjmfoodie
A very quick summary quiz on factors of production via http://www.dineshbakshi.com – click here
Unemployment Part 1
Aug 18th
Syllabus requirements (first part):
Unemployment
• Full employment and underemployment
• Unemployment rate
• Costs of unemployment
• Types of unemployment
• structural
• frictional
• seasonal
• cyclical/demand-deficient
• real wage
(Macro) Episode 18: Unemployment by mjmfoodie
(Macro) Episode 19: Types of Unemployment by mjmfoodie
Unemployment – Description of different types by jcsballoon
The Multiplier, Accelerator and Crowding Out
Aug 17th
These are Higher Level Extension Topics, and are listed in the following way on the 2005 IB syllabus:
• Multiplier
[including calculation of multiplier]
• Accelerator
• “Crowding out”
Here are some video resources and questions to help you understand these concepts.
Watch the following video and then answer the questions underneath.
MPC and the Multiplier by FitzEcon
1) Define the MPC?
2) What is the formula for the multiplier?
3) Define the MPS.
4) Record, in writing / notes, the example given by the speaker.
5) Extension – Check your text book’s entry and enhance your explanation of the multiplier, with particular attention to the concept of ’rounds’
Fiscal policy and the multiplier effect by pajholden
6) Why, in the example given, does the government want to boost Aggregate Demand?
7) What would be the trade-off of this economic goal?
8] Demonstrate the above on a sketch diagram.
9) What two fiscal policy options does the government have?
10) What does the theory of the multiplier effect state? (add to previous explanation)
11) Briefly summarise the example given of how an initial increase in spending on healthcare by the government leads to further increases in AD.
12) What are the difficulties mentionned which are associated with the multiplier effect?
13) Extension – think about it – why might cutting tax be different in terms of the impact on the multiplier compared to increasing government spending by the same amount of money?
MEC and Accelerator investment theories by pajholden
NOTE You only need to focus on the Accelerator Theory (4 mins 16 secs onwards) for HL IB Economics (although it is harmless to view the MEC theory section)
14) What are the two types of investment mentionned – explain the difference.
15) What is the Accelerator Theory in basic terms.
16) Enhance your notes by checking your text book and following links:
http://tutor2u.net/economics/revision-notes/as-macro-multiplier-accelerator.html
Bottom of this page: http://econ.la.psu.edu/~dshapiro/l18nov04.htm
http://cafehayek.com/2010/02/crowding-out.html
Crowding Out
Research and summarise information to include the following features under the topic of ‘crowding out’. Two useful videos and a slideshow are given at the end.
- Definitions
- Explanation of what it is
- Examples
- Diagrams
- Outline the difference between complete, partial and no crowding out.
(Macro) Episode 27: Crowding Out & Lags by mjmfoodie
Note that from c. 2mins 50 secs moves on to time lags – it is good revision of this separate topic!
A helpful animated slideshow:
Crowding Out Effect by reffonomics.com – click here
And finally, this is pure genius! …
Crowding-Out Effect Song (Heavy Metal Edition) by medicotube
Revise IGCSE Economics
Apr 25th

Image: Some rights reserved by hirejoejohnson
IGCSE and GCSE Economics Section on Dinesh Bakshi’s site.
i-Study Students’ Page – Revision Material includes Interactive Games
i-Study IGCSE Economics main page – click on the section buttons to see revision material
A revision Document can be downloaded here via the The Business –TES wiki
Very, very condensed revision notes (hosted on Bangkok Patana School’s server, but be aware that these notes follow an older syllabus, so check the headings against the current syllabus)

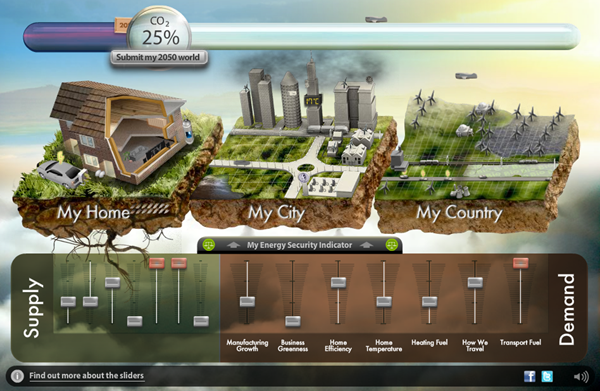
Can you drastically cut UK carbon emissions by 2050?
Mar 9th
Could you take charge and organise changes in production and consumption to cut UK CO2 production in 2050 to 20% of 1990 levels?
This excellent interactive decision making exercise asks you to do just that. It has great potential in geography, economics, environmental science and more.
Interestingly, if you get it right (succeed in hitting the 20% target or lower), you can submit your ‘decisions’ and the Department of Energy and Climate Change will combine your data with all other submissions to help inform a debate about the kinds of “choices and trade-offs the United Kingdom faces to reach the 2050 emissions reduction target”.
Hit the link below:
Thanks to my friend and former colleague, Andy, for passing this my way.
Market Failure
Mar 8th
Introduction to Market Failure
Let’s kick off with mjmfoodie:
economicshelp gives us this video:
Another simple overview of how markets fail for merit and demerit goods (S and D curves used)
BrynJonesOnline:
More complicated overview of market failure using concept of marginal costs and marginal benefits.
richardmckenzie covers welfare loss and briefly introduces solutions at end.
(1 of 2)
(2 of 2)
Externalities
From mjmfoodie:
Follow this link:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S0lH4GEFy1o
Simple Overview of how markets fail for merit and demerit goods (S and D curves used) by BrynJonesOnline
Lighthearted and simple overview of some solutions to negative externalities by ASEconomics
Some student work on the topic:
Public Goods
by mjmfoodie