A Song about Elasticity
Oct 28th
Some people have a lot of time on their hands, but we should sometimes be grateful for that … this song summing up the different elasticities is worth a listen (you never know, it might even help you revise this particular topic …)

Cross Price Elasticity and Income Elasticity
Oct 25th
1) Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
A video from pajholden (click on the image below – this video can’t be embedded).
Image: ![]() Some rights reserved by avlxyz
Some rights reserved by avlxyz
2) Income Elasticity of Demand
A video from pajholden (click on the image below – this video can’t be embedded).
Image: ![]() Some rights reserved by AngelalalaChan
Some rights reserved by AngelalalaChan
3) Both XED (Cross Price Elasticity of Demand) and YED (Income Elasticity of Demand)
The Effects of Price Controls
Oct 5th
This section of the IB syllabus requires you to understand the following:
- Maximum price: causes and consequences
- Minimum price: causes and consequences
- Price support/buffer stock schemes
Before learning about these concepts, it is first worth being sure of the following concepts:
- Consumer Surplus
- Producer Surplus
The rest of this post gives you links to online resources to help you become an expert in these concepts. Make sure you consult your text book(s) too, to provide further understanding.
Consumer and Producer Surplus
http://welkerswikinomics.wetpaint.com/page/Consumer+and+Producer+Surplus
Maximum prices and Minimum prices : causes and consequences
http://tutor2u.net/economics/revision-notes/as-marketfailure-maximum-prices.html (although you may not understand all of this yet – the bits on elasticity for example)
http://tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/marketsinaction/black_markets.htm
http://www.fmhs.auckland.ac.nz/faculty/ltu/toni_ashton/supply-demand.swf [sections 7 and 8]
http://welkerswikinomics.wetpaint.com/page/Application%3A+Government-Set+Prices
Price support/buffer stock schemes
Supply and Demand Interacting – The Equilibrium Price
Sep 28th
Understand Demand? Understand Supply? Now we need both hands to clap, and when we put them together we can understand how prices are arrived at when market forces are left to their own devices (and also when they’re not). What Adam Smith called the invisible hand … you need to know this concept like the back of your own (not so invisible) hand.
![]() Quite a lot of video tutorials on this fundamentally important economic concept.
Quite a lot of video tutorials on this fundamentally important economic concept.
Probably the best way to start (again) – take it away mjmfoodie:
Perhaps more detailed, jodiecongirl tackles market equilibrium:
But for an even deeper level of detail, here are two videos by richardmckenzie (note his tutorials are geared towards an MBA course!):
![]() http://www.whitenova.com/thinkEconomics/supply.html
http://www.whitenova.com/thinkEconomics/supply.html
![]() Now that you have hopefully grasped the fundamentals, it is worth checking your understanding further through these interactive tutorials:
Now that you have hopefully grasped the fundamentals, it is worth checking your understanding further through these interactive tutorials:
http://hadm.sph.sc.edu/courses/econ/sd/sd.html
Notice that the above tutorial continues on to another page:
http://hadm.sph.sc.edu/courses/econ/sd/SD3.html
![]() There are two good podcasts publishes by Biz/Ed which also include transcripts and possible questions:
There are two good podcasts publishes by Biz/Ed which also include transcripts and possible questions:
Supply
Sep 27th
Introduction and summary by MJMFoodie:
jodiecongirl runs through the determinants of supply:
jodiecongirl explains movements along and shifts of the supply curve:
Follow up activities to check your understanding:
Original MS Powerpoint file here
Causes of Inflation
Sep 14th
MJMFoodie overview:
1) Monetary Inflation
Watch the first part of this video until 1 minute 30 seconds in (you can watch the rest for a historical example of inflation in the US, but this is not essential to our understanding at this point)
2) Demand Pull and Cost Push Inflation
Introducing Demand
Sep 13th
![]() EXCEL spreadhseet to explore / predict how a demand ‘curve’ might work.
EXCEL spreadhseet to explore / predict how a demand ‘curve’ might work.
MJMFoodie video introducing demand:
Slideshow to prompt discussion / thought around the different variables that might move the demand curve. [IB students should know how this relates to the concept of ceteris paribus (look it up) and that changes in these variables are breaking the ceteris paribus assumption. IGCSE students need not worry too much about this.]
Link to original MS Powerpoint here.
If you need to review this, see the video on determinants of demand by jodiecongirl
These changes cause the entire demand curve to shift either to the left or the right.
MJMFoodie video on change in demand versus change in quantity demanded
![]() Check the difference between “movements along" and “shifts of” the demand curve by exploring these interactive examples:
Check the difference between “movements along" and “shifts of” the demand curve by exploring these interactive examples:
Changes to the Demand Curve at www.joehoy.com
![]() You need to be really clear that demand is different from quantity demanded. This interactive tutorial by www.reffonomics.com should emphasise this even more:
You need to be really clear that demand is different from quantity demanded. This interactive tutorial by www.reffonomics.com should emphasise this even more:
The Difference Between Quantity Demanded and Demand
Also, jodiecongirl gives an excellent summary on changes in demand and shifts of the demand curve:
Once you think you have understood the concepts introduced above, here are some activities to attempt on line to check and consolidate your understanding.
 Economics Interactive Tutorial by Sam Baker at the University of South Carolina
Economics Interactive Tutorial by Sam Baker at the University of South Carolina
![]() Visit this animation and explore it to answer the following questions:
Visit this animation and explore it to answer the following questions:
http://www.bized.co.uk/learn/economics/markets/mechanism/interactive/demand1.swf
The diagram shows the amount consumers would like to purchase at a price of £5 (32) What happens in the following cases?
- Price rises to 8
- Price rises to 9
- Price falls to 3
- Price falls to 1
Explain why people may react in the way you have observed.
[Activity taken from http://www.bized.co.uk/learn/economics/markets/mechanism/interactive/part1.htm]
The Circular Flow Of Income
Sep 9th
![]() To view an excellent introductory animation to introduce the concept of the circular flow of income, visit this page from the excellent Macroeconomics, Manfred Gärtner, Resources For Students site. A large copy of the same flash file is here.
To view an excellent introductory animation to introduce the concept of the circular flow of income, visit this page from the excellent Macroeconomics, Manfred Gärtner, Resources For Students site. A large copy of the same flash file is here.
![]() A couple of youtube videos should also help explain this model.
A couple of youtube videos should also help explain this model.
First the long one:
Source: lousycracker
And now a shorter video:
Source: BrynJonesOnline
Source: jodiecongirl – best suited to A-Level or IB students
Video: Circular Flow of Income – Macroeconomics [pajholden – best suited to A-Level or IB students]
![]() Once you think you’ve begun to understand it, you can explore an interactive circular flow for yourself, also from the above mentioned Manfred Gärtner site. Click here.
Once you think you’ve begun to understand it, you can explore an interactive circular flow for yourself, also from the above mentioned Manfred Gärtner site. Click here.
![]() S-Cool website gives quite a detailed explanation, best suited to A-Level or IB students here.
S-Cool website gives quite a detailed explanation, best suited to A-Level or IB students here.
The Economic Health Of A Country
Aug 26th
[License: Some rights reserved by juhansonin]
As we begin to explore macroeconomics, it is worth thinking about some of the key things that we will be looking at and how they apply to a real life country.
Economists agree that there are four main macroeconomic goals which most governments consider when managing their economy (and some governments, as we know, manage their economies more directly than others). The four macroeconomic goals are:
1) Growth (an increase in the country’s total output)
2) Low Unemployment (or put another way, high employment)
3) Stable General Price Level (while it is accepted that a small amount inflation is manageable, both high inflation and deflation are seen to be undesirable).
4) A Healthy Balance of Payments (for example, importing more goods and services than those that a country exports can be seen to be undesirable in the long run).
Sometimes, a fifth macroeconomic goal is added, although we should recognise that it clearly appears to be of variable importance to the different governments of the world:
5) Equity (an even distribution of wealth within the country)
There are other macroeconomic goals that are sometimes considered which you may come across in your research.
A good research task is to consider these macroeconomic goals for a country and gather data on a number of economic indicators for your country. Examples of such indicators include:
- GDP and / or GNP
- GDP per capita / and or GNP per capita
- Rates of Inflation
- Interest Rates
- Unemployment Levels
- Balance of Trade (Imports versus Exports)
- Distribution of Wealth
You could choose a country that has signed up to the OECD. What does that stand for, and why would a country want to belong to this organisation?
Look at the economic health for your chosen country over the past ten years. Gather text, images and even video links to support your findings. If you can, try to see why they changes but don’t worry about this too much – this can be complicated and we haven’t even studied the theory yet.
A great way to present your findings would be to produce a ‘glog’ or online poster. You can host your glogs at http://www.glogster.com/ and teachers can even set up accounts for their class here: http://edu.glogster.com/
Make your glog as informative as possible. Try to mix up text, images, graphs and tables and possible short video clips (from youtube for example). Remember to give a title and explain your chosen country’s membership of the OECD.
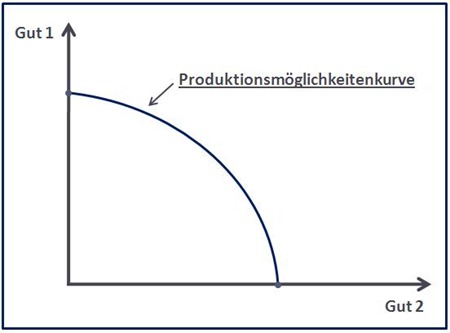
Introduction to Economics Part 2 – Production Possibility Frontiers (or PPFs)
Aug 23rd
[Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:WikiAbb1_1.JPG]
These can sometimes be referred to as Production Possibility Curves (PPCs), to reflect their shape. Frontier is a better word to use … you will need to think about what it is that the term frontier implies.
This session assumes you have a basic knowledge of PPFs already and points you to resources to help strengthen your understanding of this important concept.
This link is very good for explaining
a) the reason that the PPF is a curve and not a straight line
b) how opportunity cost increases as an economy tends to specialise in one of the two goods
http://tutor2u.net/economics/content/topics/introduction/ppfs.htm
If you feel that you need to understand these concepts even further, read the following link. Note that this introduces the idea of an outward shift of the PPF. You can ignore section C which we look at later in the course (especially Higher Level candidates)
http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/economics2.asp
The concept of increasing opportunity cost is shown very visually here:
http://itc.boisestate.edu/mediashowcase/media/prodpossfron_audio.swf
… and this animation also emphasises outwards shift – two scenarios are given – what is the difference between them?
http://webcom2.grtxle.com/Source/uploads/Economics1.swf
You should now be in a position to work through the questions associated with the interactive PPF on the website below:
http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/007334365x/student_view0/chapter2/interactive_graph_2.html
Finally, it could be worth recapping these concepts by visiting the video links below:
1) pajholden explains the PPF on youtube:
Production Possibility Frontiers by Paul Holden
2) Another human explanation:
See it in full: http://blip.tv/play/AceTJY6iSw
Finally – what assumptions does the PPF make? Try and list as many as possible and then consider how realistic these assumptions are – given reasons or examples as to why they may be unrealistic.