IGCSE Economics

Understanding the Balance of Payments
Jan 25th
This can be a difficult concept to understand (especially at IGCSE level, less so at IB level), mainly because we are trying to understand how an entire country manages its financial accounts of all transactions between itself and other countries. The real difficulty, i find, is that different nations take different approaches which means that there is no uniform ‘model’ of what Balance of Payments should be structured. In some cases, different phrases are used for the same thing (always a source of frustration to students when learning something first time round). Text books and online articles (try this and here) have plenty to say about it, but here are a few resources designed to help simplify understanding.
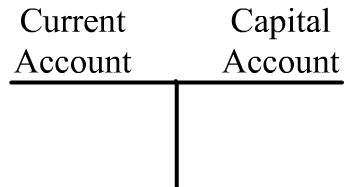
Here is a skeleton outline of the B of P, which is perhaps oversimplified. A student in my class typed notes from my whiteboard scrawl (thanks Jonathan):
This youtube video by pajholden helps understand the Current Account structure from a UK perspective: ‘balance of payments – structure of the current account ‘
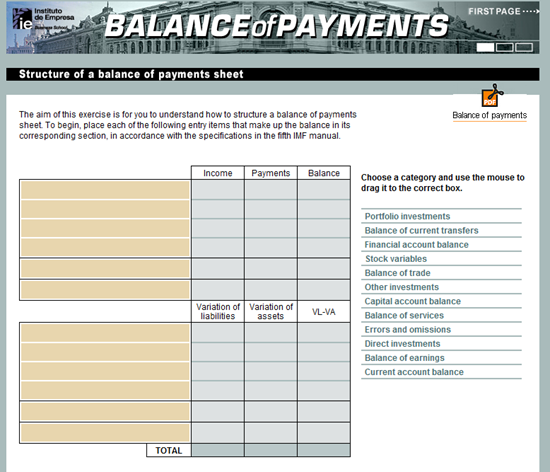
Below, this simple interactive drag and drop exercise hosted at www.reffonomics.com is a useful reminder of how different ‘components’ of the Balance of Payments can be classified. Click on the table / image below.
Below, there is another really helpful interactive exercise by Rafael Pampillon hosted at http://openmultimedia.ie.edu to play around with the different components of the Balance of Payments, where they might be placed and how they might be applied. You are advised to read the guide attached to the .swf file (top right hand corner) but even if time does not allow for this, it is good to experiment as the feedback will help you realise the correct answers with a bit of trial and error). Click on the image below to access the page.
Finally, here is a bit more detail from http://tutor2u.net on the topic (better for IB level than IGCSE level):
http://tutor2u.net/economics/revision-notes/as-macro-balance-of-payments.html
Understanding Comparative Advantage
Dec 7th
Having played the desert island game, you should be in a position to develop your understanding of an important economic concept which is used to support international trade. 2 videos should help. The first is a rough-and-ready video with an easy to access example:
Now, MJMFoodie gives an old but polished example, and introduces Adam Smith and David Ricardo’s perspectives on these matters:
Trade Unions
Dec 3rd
The IGCSE Economics syllabus requires you to:
- describe trade unions and their role in an economy;
Watch the following videos and answer these questions:
- What roles do Trade Unions have in the economy – what do they do?
- What are the possible advantages of Trade Unions?
- Detecting bias – Are these videos in favour of unions? or against?
Now research some of the possible arguments against Trade Unions from an economic perspective …

Economics Game: Ricardo, Coconuts and A Desert Island
Dec 2nd
This is a good online game (you need Flash player in your browser) to learn about and develop your understanding of the concept of Comparative Advantage.
Great for IB Economics students, and possibly handy for IGCSE level students too.
Image: Some rights reserved by Dana Moos, Realtor
Play the game here: http://desertislandgame.com/
Extra: By the way, the name of the guy you play is Ricardo and, in case you don’t already realise, this is significant. Look the name David Ricardo up (on wikipedia for example) and find out why.

What Are Supply Side Policies?
Nov 23rd
Image: Some rights reserved by Re-Entry One Stop
![]() Here is a simple activity that could be completed as a class.
Here is a simple activity that could be completed as a class.
Visit this site to see a list of 12 supply side policies:
http://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/economic-growth/supply-side-policies.html
In pairs or ones, create a cartoon to explain one policy from the list of 12. Your cartoon should be designed to make the idea easy to understand.
Remember to add speech bubbles and appropriate characters / setting to give the policy some meaning. Add a title that matches the policy itself.
I recommend you use toondoo which is easy to use and quick and free to sign up for.
If you use this particular piece of online software, you can share it as a public comic book so that it can then be embedded on a website.
Looking for an example of toondoo? Here is a great cartoon by my colleague Maree (this one introduces three different economic systems):
‘Eat Local ‘ Government Advertising Domestic Produce
Nov 9th
Why would a government encourage consumers to ‘buy local’?
What impact would this have on the demand / supply diagram for these products?
How could this be considered a form of protectionism?
IB Economics: Why might a government introduce this together with certain price controls (such as a minimum price / Buffer stock programme)?
How does elasticity of supply and demand affect incidence of tax?
Nov 2nd
pajholden explains the effect of indirect taxation. Note he concentrates mainly on specific tax but includes a brief section on ad valorem (percentage) tax later on. Click below.
A much longer (and therefore detailed) video by jodiecongirl. Use these if you really haven’t yet understood the key concepts, as these will take you through it slowly and step by step.
She also goes into depth about the impacts on producers and consumers in the following videos but this gets quite complex. (more suited to IB level):
General Rules About Taxes Part 1
General Rules About Taxes Part 2
A much briefer summary is here by agsmandrew and he manages to explore the impact on consumer and producer surplus (including deadwight loss) (good for a quick revision for IB students):
Visit this site and explore different possibilities on a supply/demand graph with varying levels of tax applied. Try answering the questions at the bottom. (Note – the graph also refers to Efficiency Loss which is not actually required on the IGCSE syllabus, but is necessary to IB Economics).
![]() McConnell Brue Economics – Online Learning Centre – Interactive Graphing Exercise – Tax Incidence
McConnell Brue Economics – Online Learning Centre – Interactive Graphing Exercise – Tax Incidence
Price Elasticity of Demand
Oct 30th
Introductory Videos
Video: Price Elasticity of Demand – part 1 by pajholden
Video: Price Elasticity of Demand – part 1 by pajholden
Interactive Tutorials
Economics Interactive Tutorial by Samuel Baker (Univ of Carolina)
Elasticity — A Quantitative Approach by Samuel Baker (Univ of Carolina)
The Market System – Part 1 on biz/ed – contains section on PED towards end
Price elasticity of demand and basic application in Excel by Tushar Mehta
The following videos deal with the important concept of how price elasticity of demand relates to total revenue. They cover similar ground so you may not feel the need to watch all of them, but they do take different approaches in presentation.
Price Elasticity & Total Revenue by BrynJonesOnline
Total Revenue and Elasticity by ElmagicRonaldo
Elasticity and Revenue by jodiecongirl
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) – own price elasticity by economicsfun
Good real life example on the determinants (factors affecting) Price Elasticity of Demand … ‘gasoline’ (or petrol):
In Summary
Price Elasticity: From Tires to Toothpicks (Econedlink)
Price Elasticity of Demand (tutor2u)
Price Elasticity of Demand (Welker’s Wikinomics)
(Welker’s Wikinomics)
Finally, before moving on to Price Elasticity of Supply, this 15 minute video explaining an unusual ‘spike’ in gas prices in the US in 2002, is excellent and highly recommended for applying the theory to a real life example (the latter part gets a little bit tricky, but still recommended for IGCSE and IB students):
Output– Definitions of GDP
Oct 28th
These mjmfoodie videos are very useful for understanding the concepts of GDP, real GDP (as opposed to nominal/money GDP) and growth.