about 15 years ago - No comments
The first video in this post goes to a student. Komilla (CuteChadz)has produced a very professional looking summary and it is well worth a look: pajholden does price discrimination richardmckenzie gives us two videos: Click here to see a Reffonomics interactive presentation on price discrimination. For a bit of fun, view the scene from the…
about 15 years ago - No comments
IB Syllabus requirements: • Assumptions of the model • Collusive and non-collusive oligopoly • Cartels • Kinked demand curve as one model to describe interdependent behaviour • Importance of non-price competition • Theory of contestable markets BrynJonesOnline introduces the theory before moving onto Kinked Demand Theory: Cartels This helpful video is by richardmckenzie Non Collusion…

about 15 years ago - No comments
Here is the IB syllabus requirement for this sub-topic: Monopolistic competition • Assumptions of the model • Short-run and long-run equilibrium • Product differentiation • Efficiency in monopolistic competition From www.reffonomics.com a useful introductory slide on calculating price and quantity under monopolistic competition scenario: Which then leads to finding profit (from the same site, www.reffonomics.com)…

about 15 years ago - No comments
The IB syllabus requirements for this sub-topic are to understand: Assumptions of the model Sources of monopoly power/barriers to entry Natural monopoly Demand curve facing the monopolist Profit-maximizing level of output Advantages and disadvantages of monopoly in comparison with perfect competition Efficiency in monopoly Here are a selection of useful resources to further your understanding…

about 15 years ago - No comments
The IB Economics syllabus requires you to understand the following: • Assumptions of the model • Demand curve facing the industry and the firm in perfect competition • Profit-maximizing level of output and price in the short-run and long-run • The possibility of abnormal profits/losses in the short-run and normal profits in the long-run •…
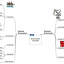
about 15 years ago - No comments
www.bized.co.uk provides some useful materials for this topic. The starting point is their mind map. Click below to view the mindmap on its original site and in full. A very useful MS powerpoint file, also courtesy of www.bized.co.uk, to expand on teh above mindmap can be accessed here: pajholden gives an overview in 8…
about 15 years ago - No comments
We need to understand this according to the syllabus: Distinction between normal (zero) and supernormal (abnormal) profit Profit maximization in terms of total revenue and total costs, and in terms of marginal revenue and marginal cost Profit maximization assumed to be the main goal of firms but other goals exist (sales volume maximization, revenue maximization,…

about 15 years ago - No comments
By now you should understand the graphs for a) Total Product (b) Average and Marginal Product (c) FC, VC and TC (d) AFC, AVC, ATC, MC You should also recognise the ultimate assumption of firms – profit maximising Now we turn to revenue. Image: Some rights reserved by saturnism You now need to: Recap on…

about 15 years ago - 2 comments
Our eventual aim of this learning session is to understand (and know ‘like the backs of our hands’) the following diagram: First we need to understand the difference between fixed and variable costs. This video by MJM Foodie handles this well: This is a very good interactive exercise to consolidate your understanding of the different…

about 15 years ago - No comments
a) Find out the definition for the short run (in Economics it has a specific definition). Use google and the define: prefix. Image: Some rights reserved by °Florian b) A practical activity in the classroom. Rules: 1) A wall in the classroom – you can not move away from the wall, you must always stay…








