Posts tagged output

Output or ‘Product’ in The Short Run
Nov 25th
a) Find out the definition for the short run (in Economics it has a specific definition).
Use google and the define: prefix.
Image: Some rights reserved by °Florian
b) A practical activity in the classroom.
Rules:
1) A wall in the classroom – you can not move away from the wall, you must always stay right next to the wall. Physical land is fixed.
2) At one end of the wall a desk with a pile of raw-material-paper (or text books).
3) At the other end of the wall a desk. This is where the paper is manufactured into end-of-wall paper once it has been transferred from the other side to this desk.
4) Only one piece of paper can be carried by a worker at a time.
5) We will add more and more workers, but since no-one can move away from the wall, they can not pass each other.
6) Each production cycle (period of time) lasts one minute only.
7) All workers recognise the profit-maximising incentive of working to full ability, and behave accordingly. (No slacking …)
6) First volunteer up. Results will be recorded on a Google Spreadsheet. Access the one below and make a copy of it in your Google Account.
Direct link (make a copy in your own google account): Opengecko Product Exemplified – Carrying Books Exercise
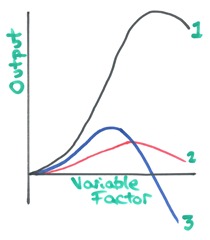
c) Make sure you have thoroughly discussed the graphs – what is happening? Why do they have these shapes?
d) Research (text book and / or web) the definitions of, behaviour of and relationship between the following as the one factor of production (labour) is increased:
- total output [total product]
- average output [average product]
- marginal output [marginal product]
Key phrase: diminishing returns (define and be precise about the full phrase)
Your ultimate aim is to be able to identify the 3 curves below and explain them:
e) Review your understanding of the above with the following videos:

Output or ‘Product’ in The Short Run
Nov 23rd
a) Find out the definition for the short run (in Economics it has a specific definition).
Use google and the define: prefix.
Image: Some rights reserved by °Florian
b) A practical activity in the classroom.
Rules:
1) A wall in the classroom – you can not move away from the wall, you must always stay right next to the wall. Physical land is fixed.
2) At one end of the wall a desk with a pile of raw-material-paper (or text books).
3) At the other end of the wall a desk. This is where the paper is manufactured into end-of-wall paper once it has been transferred from the other side to this desk.
4) Only one piece of paper can be carries by a worker at a time.
5) We will add more and more workers, but since no-one can move away from the wall, they can not pass each other.
6) Each production cycle (period of time) lasts one minute only.
7) All workers recognise the profit-maximising incentive of working to full ability, and behave accordingly. (No slacking …)
6) First volunteer up. Results will be recorded on a Google Spreadsheet. Access the one below and make a copy of it in your Google Account.
Direct link (make a copy in your own google account): Opengecko Product Exemplified – Carrying Books Exercise
c) Make sure you have thoroughly discussed the graphs – what is happening? Why do they have these shapes?
d) Research (text book and / or web) the definitions of, behaviour of and relationship between the following as the one factor of production (labour) is increased:
- total output [total product]
- average output [average product]
- marginal output [marginal product]
Key phrase: diminishing returns (define and be precise about the full phrase)
e) Review your understanding of the above with the following:
Output– Definitions of GDP
Oct 28th
These mjmfoodie videos are very useful for understanding the concepts of GDP, real GDP (as opposed to nominal/money GDP) and growth.
Output, Costs, Revenue and Profit
Feb 1st
[Image: nDevilTV  Some rights reserved]
Some rights reserved]
The Cambridge IGCSE syllabus requires us to have a good understanding of the following:
We have seen useful videos on YouTube before, particularly MJMFoodie’s very visual explanations (which are often aimed at higher stages of education, such as IB). One of her useful videos (on fixed and variable costs) is here:
Another useful video by MJMFoodie gives an introduction to the topic and explains the idea of the law of diminishing returns.
A great idea for a learning activity to really understand this topic is for you to work with one other person towards producing your own video, MJMFoodie style. It should be simple – create a PowerPoint (or similar) with images. These images can be your own that you have drawn on the computer, scanned into the computer, or other images produced by other people. It is obviously preferable to use images that are not copyrighted, so some good places to visit for non-copyright images are here:
http://www.everystockphoto.com/
http://search.creativecommons.org/
As you assemble your slideshow, make sure you are working on your script to go with each slide. Later on you will want to record your voiceover while playing the slideshow. In that case, planning the video out is essential and you should start with your partner by story-boarding the video.
Your video should summarise this theory on costs, revenue and profit as outlined in the syllabus above. It should summarise it in a highly visual and accessible way. Your video should ideally last somewhere between 5 and 10 minutes.
A good starting point is to consult the relevant chapter in the text book you are using. A good text book is this one, which introduces the idea using Sue’s Teddy Bear Firm.
 |
Economics: A Complete Course for IGCSE and O Level: Endorsed by University of Cambridge International Examinations |
Other simple summaries of aspects of this topic are found here:
Tutor2U – Simple Overview of Output, Fixed Costs and Variable Costs
Tutor2U – Simple Overview of Revenue, Costs and Profit
Tutor2U – Simple Overview of Average Costs and the Scale Of Production