Posts tagged trade
The Marshall Lerner Condition and the J Curve
Dec 11th
1) A good web page, by http://welkerswikinomics.com:
The Marshall-Lerner Condition, the J-curve, and the US trade deficit
2) A useful video via the same author’s http://www.econclassroom.com:
3) A chance for you to play around with the Marshall Lerner condition yourself:
http://www.eco.rug.nl/~gigengack/ge/ML_Interactive/ML_Interactive.htm
Purchasing Power Parity
Dec 7th
Purchasing Power Parity by Mindbitesdotcom. This is an incomplete taster / ad for a course you have to subscribe to, but is still useful as is stands, provided you add to your understanding with other resources.
15: PURCHASING POWER PARITY by InformedTrades:
2 Useful web sites:
http://economics.about.com/cs/money/a/purchasingpower.htm
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-purchasing-power-parity-theory.htm
Questions:
1) What is PPP and explain how it works using a hypothetical example?
2) Evaluate the usefulness of PPP theory when applied to the real world.
World Trade Organisation (WTO)
Nov 16th
The syllabus requirements:
4.4 World Trade Organization (WTO)
• Aims
• Success and failure viewed from different perspectives
Accordingly, your goal from learning about this part of the syllabus should be to be able to answer the following questions:
1) What are the aims of the World Trade Organisation?
2) What are some of the positive contributions of the World Trade Organisation to the world trading system? Evaluate these advantages and, in particular, identify the stakeholders who would agree that these are advantages with reasons for their agreement.
3) What are some of the criticisms made against the World Trade Organisation? Evaluate these advantages and, in particular, identify the stakeholders who would agree that these are disadvantages with reasons for their disagreement.
Image: Some rights reserved by World Trade Organization
A flash-based slideshow courtesy of the guardian gives an historical introduction:
This infographic by http://www.themoscownews.com sums up the main aims of the WTO:
History and functions of the World Trade Organization (WTO)
The ever reliable mjmfoodie gives us a introduction to GATT, which later became WTO. It gives us the history, moving on to the reasons for the WTO (aims). It is quite pro-WTO in its approach:
Episode 37: GATT/WTO by mjmfoodie (4’ 38”)
This is an impressive student project on the same topic which gets very detailed about membership requirements, but then moves on to the main aims of the WTO, which is useful for our syllabus requirements:
World Trade Organization by sdhettige (9’28”)
The World Trade Organisation is a documentary excerpt posted online by ![]() It is good for the historic set-up of the WTO (originally GATT – what was this?), and the various Rounds which shaped its development. It is also good for an overview of some global economic developments (such as the 1970s World Oil Crises) that are useful to know about in general for IB Economics.
It is good for the historic set-up of the WTO (originally GATT – what was this?), and the various Rounds which shaped its development. It is also good for an overview of some global economic developments (such as the 1970s World Oil Crises) that are useful to know about in general for IB Economics.
This next video is an engaging infographic on some of the difficulties faced by Kenya. Kenya’s WTO membership required in trade liberalisation (reduction of protectionism). This video is biased, but puts forwards some pretty clear arguments against the imposed trade regulations placed by rich Western/Northern economies, which some argue the WTO simply supports at the expense of poorer economies such as Kenya. Remember, the syllabus expects us to see the issue from different perspectives.
Animation: Trade Justice – why world trade rules need to change by tradeaid (2’ 28’”)
Michael Moore is a renowned political commentator/critic famous for a number of documentary films. In this clip he is clearly very critical of the WTO, giving a more extreme view of its possible ‘failure’:
Michael Moore by ProtestGlobalisation
Next we have short interview clips with various stakeholders in the Philippines, giving strong criticism of the potential effects of trade liberalisation, as actively encouraged by the WTO, on such a LDC.
Why WTO is Bad for Developing Countries by ymataglenn (3’ 46”)
Finally, ‘CuteChadz’, a student, sets out her own revision-focused overview of the World Trade Organisation:
A2 Economics: World Trade Organisation (WTO) in 8 mins by CuteChadz
Trading Blocs
Nov 10th
IBO 2005-2012 Syllabus Requirements:
Trading blocs
• Free trade areas (FTAs)
• Customs unions
• Common markets
Higher level extension topics
• Trade creation and trade diversionObstacles to achieving integration
• reluctance to surrender political sovereignty
• reluctance to surrender economic sovereignty
Introduction to Trading Blocs
Episode 38: Trade Blocs by mjmfoodie
Perhaps a simpler introduction is here:
Trading Blocs by LanternaEducation
A more discursive explanation by student CuteChadz …
A2 Economics: Trade Blocs by CuteChadz
Trade Creation and Trade Diversion
Towards the end of the previous video, there was reference to trade creation and trade diversion, although the explanation was quite simple. You can get more depth out of these two effects of economic integration (the formation of trade blocs). The following two websites are recommended for reading up on these two topics:
http://tutor2u.net/economics/revision-notes/a2-macro-trade-agreements.html
http://www.revisionguru.co.uk/economics/creatdiver.htm
Obstacles to Achieving Integration
Finally, for brief but useful discussion of the obstacles to achieving integration, and summary of some of the above, visit this site:
http://centralecon.wikia.com/wiki/Economic_Integration
Tariffs, Quotas and Subsidies
Oct 23rd
These three types of protectionism have pretty tricky diagrams (or at least they can get tricky if we want to really get into how they work in terms of the impact they have on different groups or stakeholders. Note – we should want to get tricky if we want to do well at IB Economics ![]() ). Here is a round up of resources to help you understand their effects.
). Here is a round up of resources to help you understand their effects.
Remember to first find a good working definition of each of these types of protectionism. Go on … Google them ![]()
An overview of the three types is here, although the ‘Next’ function does not work.
There is an excellent summary of the relevant theory here by Evan Schmidt on his impressive blog (http://schmidtomics.blogspot.com/)
Tariffs
Here’s what a diagram might look like. It gives a good idea of the complexity of the diagram:
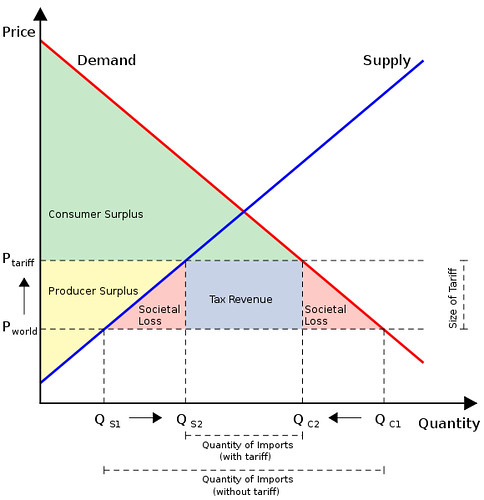
Image: Some rights reserved by Gaynoir_
However, I recommend you refer to ‘welfare loss’ instead of ‘societal loss’ – whatever the term you use, these pink triangles represent inefficiency. I also recommend you use letters for the different ‘shapes’ rather than colours, as that is far more efficient to complete in an exam and to refer to in your text which you use to explain the diagram. This diagram below uses letters, but note, you can (should) still get even more sophisticated than this – check your IB Economics text book if you have one.
Image by Ratibgreat on wikipedia
This first video by lostmy1 is a simple explanation compared to the following videos, but it is very accessible. It does not tackle efficiency / consumer and producer surplus, and these are concepts which you should then try to understand from the subsequent videos.
This next video by economicsfun is a very good explanation. The second half moves on to analysing in terms of theoretical numbers, which would not be necessary in an IB Economics essay – but being able to identify the different ‘shapes’ which the author colours in would be ideal if you used a lettering system (as is likely to be the case in your text book).
This video by pajholden can not be embedded, but is worth hitting the link below for a further explanation:
tariffs and protectionism by pajholden
Probably the best of the bunch, MechamDee gives us a video with quiet audio, but it is thorough, starting off with the effect of trade compared to non-trade and then moving onto the impacts of tariffs. He gets in to detail with the different ‘shapes’ as letters, although the image itself is small and not so easy to see. It is very well explained though:
These interactive presentations by http://www.reffonomics.com are particularly useful for checking your understanding:
Finally economicslessons give us a slick (and silent) animation that summarises the different effects well, but you’ll definitely want to pause this as you go along to take it in properly:
Quotas
This a particularly tricky one to revise form the internet as there are different, conflicting explanations of how a quota works in an internationally competitive market. For IB Economics, you want the diagram that shows effective supply to be a ‘kinky’ supply curve.
MechamDee gives another thorough explanation, with useful demonstration of the ‘effective’ (or ‘kinky’) supply curve.
Subsidies
What, no videos? No interactive tutorials? Sorry! Who is going to be the first to make one?
Correction: I have found an excellent video analysing the impact of a protectionist subsidy by http://welkerswikinomics.com (welkerjason):
See the full post for some accompanying questions:
Calculating the effects of protectionist subsidies – an IB HL exercise
Anyway, For additional best IB-level information on this, visit the schmidtomics link at the very top of this post, or consult your IB Economics text book!
Reasons for Trade
Sep 18th
Syllabus requirements:
Reasons for trade
• Differences in factor endowments
• Variety and quality of goods
• Gains from specialization
• Political
Higher level extension topic
• Absolute and comparative advantage (numerical and diagrammatic representations)
• opportunity cost
• limitations of the theory of comparative advantage
The first bullet points should be quite well understood by most students after a little research and careful thought.
This classic clip featuring Milton Friedman is often used as an argument for the free market, but I think it works particularly well as an argument for international (free) trade:
Power of the Market – The Pencil uploaded by LibertyPen
The Higher Level topics, particularly the concept of Comparative Advantage are trickier. However, the theory of comparative advantage is a vital argument in favour of international trade, and one well worth revising until you are confident that you understand it fully. Be sure to use diagrammatic explanations using PPFs, as well as numerical examples. Visit the following two related links in this order:
Economics Game: Ricardo, Coconuts and A Desert Island
Understanding Comparative Advantage
In addition, these excellent slideshows hosted on reffonomics.com will help you, particularly with the diagrams aspect.
Understanding Comparative Advantage
Dec 7th
Having played the desert island game, you should be in a position to develop your understanding of an important economic concept which is used to support international trade. 2 videos should help. The first is a rough-and-ready video with an easy to access example:
Now, MJMFoodie gives an old but polished example, and introduces Adam Smith and David Ricardo’s perspectives on these matters:

Economics Game: Ricardo, Coconuts and A Desert Island
Dec 2nd
This is a good online game (you need Flash player in your browser) to learn about and develop your understanding of the concept of Comparative Advantage.
Great for IB Economics students, and possibly handy for IGCSE level students too.
Image: Some rights reserved by Dana Moos, Realtor
Play the game here: http://desertislandgame.com/
Extra: By the way, the name of the guy you play is Ricardo and, in case you don’t already realise, this is significant. Look the name David Ricardo up (on wikipedia for example) and find out why.




