Posts tagged unemployment

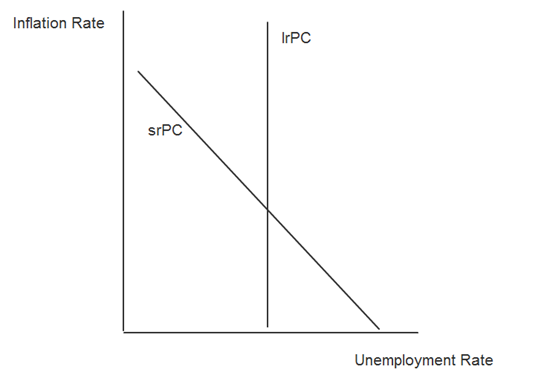
The Phillips Curve
Sep 14th
Be warned. This one’s quite tricky. We’ll rely heavily on the truly excellent http://www.reffonomics.com website for this topic, but these activities will be best used following some prior learning of the Phillips Curve. I like the approach that reffonomics take, it is thorough and helps to give a good recap of general ASAD macro models. This takes things to quite an advanced level though.
First, learn about (or recap) the topic by visiting this eye-catching interactive.
Second, run through this presentation and see if you give correct answers for the short series of questions.
Third, try your hand at this quiz.
Fourth, explore how different scenarios impact on the ASAD graph and the Phillips Curve Graph here.
Fifth, try 20 multiple choice questions here. Some of them are tricky, but you’ll get instant feedback at the end.
Lastly, try your hand at some of these activities here – have a go by moving the lines and A, B and C points, and then see the suggested answers. You might not understand how to do the first one or two, but when you see their animated answers you should hopefully begin to get the hang of it.
Advanced activity:
Step 1 – download this ‘free response’ worksheet and answer using good old pencil / ruler combo.
Step 2 – check your answers against these suggested answers.
Data Response Question – Unemployment
Sep 6th
For those studying IB Economics, this is a data response question which I created for the unemployment topic back in 2008, following the usual conventions and mark scheme requirements as closely as I could.

Photo: Some rights reserved by Saad.Akhtar
The text is adapted from an original article by The Times Online, but it does not appear to be hosted there anymore.
Click here for the question paper.
Click here for the mark scheme.
Unemployment Part 1
Aug 18th
Syllabus requirements (first part):
Unemployment
• Full employment and underemployment
• Unemployment rate
• Costs of unemployment
• Types of unemployment
• structural
• frictional
• seasonal
• cyclical/demand-deficient
• real wage
(Macro) Episode 18: Unemployment by mjmfoodie
(Macro) Episode 19: Types of Unemployment by mjmfoodie
Unemployment – Description of different types by jcsballoon
The Economic Health Of A Country
Aug 26th
[License: Some rights reserved by juhansonin]
As we begin to explore macroeconomics, it is worth thinking about some of the key things that we will be looking at and how they apply to a real life country.
Economists agree that there are four main macroeconomic goals which most governments consider when managing their economy (and some governments, as we know, manage their economies more directly than others). The four macroeconomic goals are:
1) Growth (an increase in the country’s total output)
2) Low Unemployment (or put another way, high employment)
3) Stable General Price Level (while it is accepted that a small amount inflation is manageable, both high inflation and deflation are seen to be undesirable).
4) A Healthy Balance of Payments (for example, importing more goods and services than those that a country exports can be seen to be undesirable in the long run).
Sometimes, a fifth macroeconomic goal is added, although we should recognise that it clearly appears to be of variable importance to the different governments of the world:
5) Equity (an even distribution of wealth within the country)
There are other macroeconomic goals that are sometimes considered which you may come across in your research.
A good research task is to consider these macroeconomic goals for a country and gather data on a number of economic indicators for your country. Examples of such indicators include:
- GDP and / or GNP
- GDP per capita / and or GNP per capita
- Rates of Inflation
- Interest Rates
- Unemployment Levels
- Balance of Trade (Imports versus Exports)
- Distribution of Wealth
You could choose a country that has signed up to the OECD. What does that stand for, and why would a country want to belong to this organisation?
Look at the economic health for your chosen country over the past ten years. Gather text, images and even video links to support your findings. If you can, try to see why they changes but don’t worry about this too much – this can be complicated and we haven’t even studied the theory yet.
A great way to present your findings would be to produce a ‘glog’ or online poster. You can host your glogs at http://www.glogster.com/ and teachers can even set up accounts for their class here: http://edu.glogster.com/
Make your glog as informative as possible. Try to mix up text, images, graphs and tables and possible short video clips (from youtube for example). Remember to give a title and explain your chosen country’s membership of the OECD.